eSPACE: Leveraging Theoretical Foundations for the End-User Development of Cross-Device and IoT Applications
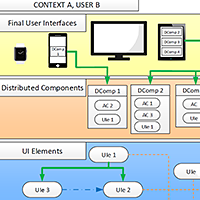
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cross-device computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), there is a need for intuitive and user-friendly solutions empowering end users to create and tailor their applications. To address this need, we analysed the different metaphors for end-user development (EUD) of cross-device and IoT applications. A key observation is the lack of addressing end user's mental models when designing interactions among devices, resulting in less intuitive EUD tools. To fill this gap, we introduce eSPACE, an end-user authoring tool facilitating the development of cross-device and IoT applications. In contrast to most existing tools, eSPACE is grounded on strong theoretical foundations, including a conceptual model, reference framework as well as design guidelines and suitable metaphors. The effectiveness of these theoretical foundations in creating an intuitive and user-friendly EUD platform has been validated in a user study. Our study confirms eSPACE's potential as a useful and easy to use tool for end-user application development. In addition, we present potential future research directions, including automation functionality, intelligibility and human-AI interaction. In discussing these future directions, we aim to foster and advance EUD research towards more end- user-accessible authoring environments for cross-device and IoT applications.
Publication Reference
Sanctorum, A. and Signer, B.: "eSPACE: Leveraging Theoretical Foundations for the End-User Development of Cross-Device and IoT Applications", ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction (TOCHI), February 2025



