From Proprietary to High-Level Trigger-Action Programming Rules: A Natural Language Processing Approach
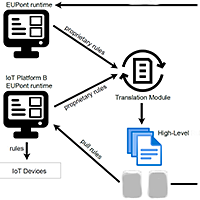
With the rise of popular task automation or IoT platforms such as If This Then That (IFTTT)}, users can define rules to enable interactions between smart devices in their environment and thereby improve their daily lives. However, the rules authored via these platforms are usually tied to the platforms and sometimes even to the specific devices for which they have been defined. Therefore, when a user wishes to move to a different environment controlled by a different platform and/or devices, they need to recreate their rules for the new environment. The rise in the number of smart devices further adds to the complexity of rule authoring since users will have to navigate an ever-changing landscape of IoT devices. In order to address this problem, we need human-computer interaction that works across the boundaries of specific IoT platforms and devices. A step towards this human-computer interaction across platforms and devices is the introduction of a high-level semantic model for end-user IoT development, enabling users to create rules at a higher level of abstraction. However, many users who already got used to the rule representation in their favourite tool might be unwilling to learn and adapt to a new representation. We present a method for translating proprietary rules to a high-level semantic model by using natural language processing techniques. Our translation enables users to work with their familiar rule representation language and tool, and at the same time apply their rules across different IoT platforms and devices.
Publication Reference
Attoh, E. and Signer, B.: "From Proprietary to High-Level Trigger-Action Programming Rules: A Natural Language Processing Approach", WISE-2023-01, arXiv preprint, October 2023



